Issue
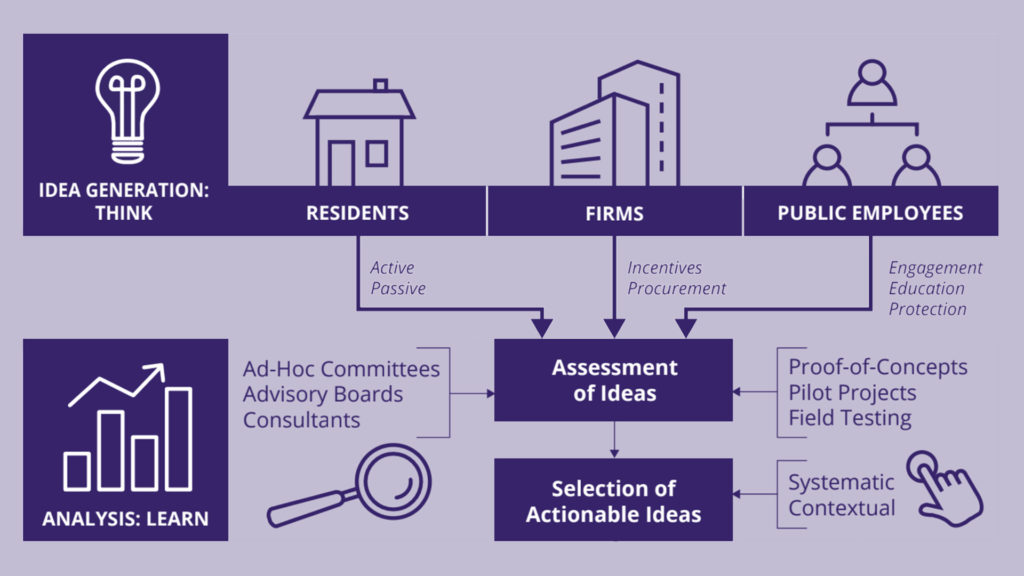
Smart cities across the US are exploring new ways to use technology and innovation to combat traffic congestion and create thriving communities with equitable access to transportation. As many Seattleites can attest to, the mobility mix is changing fast. From Uber to Waze to LimeBike, a variety of service providers are seizing the opportunity to meet transportation challenges with mobility products and shared service platforms. Thus, the city needs a way to pilot, test, and accelerate the most promising solutions on Seattle streets.
Spark
“SDOT commissioned this research with a direct intention to expand the department’s ability to make smart, data driven decisions. We are thrilled that the report not only supports the strategies outlined in SDOT’s New Mobility Playbook, but it also challenges the Department to consider more nimble and creative innovations. It encourages the use of strategic partnerships, industry best practices, and experimental piloting of new technologies through an equity lens that is inclusive all people, no matter their economic status, or zip code,” said Benjamin de la Pena, Chief of Strategy and Innovation at SDOT.
Overview
In a partnership with the Mobility Innovation Center at UW CoMotion, SDOT commissioned a study of six US cities that have been experimenting with innovative approaches to transportation management. The resulting report reveals how these leading cities have solicited new ideas, built outcome- and equity-oriented programs, and enacted change with limited public resources.
Innovation
Procurement modernization is critical for transportation innovation.
In transportation, private firms are not just vendors – they are partners that leverage critical expertise and technology to attain short- and long-term public transportation goals. How a local government “procures” goods and services from these private firms is critical—public officials must balance speed, cost, and quality with public values of fairness, equity, and transparency. For cities that want to innovate in transportation, creating a modern procurement process that is flexible and responsive to the rapid pace of technology change is a must. This research indicates that creative and well-managed procurement processes facilitate transportation sector innovation.
Materials
- Read the report
- View the press release
Impact
For SDOT to take these learnings to the next level, they will need to determine the feasibility, cost, management structure, business plan, goals, and expectations of setting up an Innovation Framework. This work should engage other frameworks operating around the world. SDOT must carefully consider whether the Innovation Framework should reside within the City or in a neutral site (like a municipal corporation or non-profit) where the City is a stakeholder and funder.
Team
The research group was led by Dr. Benjamin Brunjes from the University of Washington Daniel J. Evans School of Public Policy and Governance. The Daniel J. Evans School of Public Policy and Governance was created in 1962 as one of the nation’s first schools of public policy at a public university. Over the past 50 years, the Evans School has built a 2 reputation as one of the elite public policy schools in the nation. The school is defined by a tradition of rigorous study, innovative research, and, most importantly, a commitment to public service.
Academic Department
Faculty Leadership
Contributors
- Min Guo
- Eugene Paul


